Balance
Quinternity
Before we can build a balanced life, we have to make sure our foundation is solid. This tier focuses on five essential layers of human need—our survival, safety, connection, confidence, and growth. When one is out of sync, everything else starts to wobble.

Core-concepts
Section 5
Achieving balance across all areas of life takes more than willpower—it takes structure. Maslow’s Hierarchy offers a framework to help us identify what truly needs our attention. From the basics like food and rest to deeper desires for meaning and purpose, these five tiers help us understand what fuels our well-being.
In the modern world, it’s easy to get distracted from these essentials. We often chase productivity or external goals while skipping over the foundation. But when our core needs are out of sync, everything else feels off.
This section is designed to help you pause and reassess your priorities. What are you currently focused on? What might be missing? By reflecting on each tier—from survival to self-actualization—you’ll begin to see where your energy is going and where it may need to shift.
It’s not a ladder to climb once—it’s a rhythm to return to. Our needs evolve as life changes. Even if you’ve felt secure in one area, it’s worth revisiting. Reconnecting with your foundation helps everything else stand stronger.
Maslow's Hierarchy
Maslow's theory suggests that individuals progress through these needs in a hierarchical manner, with lower-level needs taking precedence before higher-level needs become motivating factors. However, it's important to note that this hierarchy doesn't apply universally to all individuals and cultures. Some people may prioritize different needs at different stages of life, and cultural and individual variations exist.
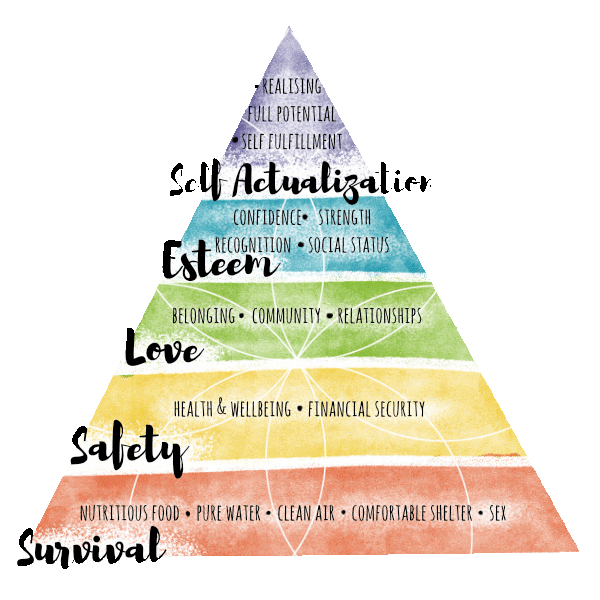
1. SUrvival Needs
These are the most basic and fundamental needs necessary for human survival.
- Food: Access to nourishment and sustenance.
- Water: Access to clean and safe drinking water.
- Shelter: Protection from the elements and a safe place to live.
- Sleep: Sufficient rest and sleep to maintain physical health.
- Air: The ability to breathe and access to clean air.
 Questions
Questions
- Where does most of my energy go when it comes to basic needs like food, water, rest, and shelter?
- Am I maintaining a rhythm that supports my physical well-being, or am I often running on empty?
- Do I spend more time fixing problems related to survival (poor sleep, low energy, disorganized meals) than preventing them?
- Are my daily choices—meals, hydration, rest—nourishing and sustainable, or reactionary and rushed?
- What area of the survival tier is most stable for me right now? Which one feels neglected?
- What small shift could help me feel more supported or energized in this tier?
Login to view.
Inspiration
![]()





 Questions
Questions